Bloodborne Pathogens Are Transmitted by Which of the Following Methods
A persons skin is penetrated by an infectious source such as an insect bite. Unprotected sex with someone who has HIV Sharing needles syringes rinse water or other equipment used to prepare illicit drugs for injection Birth to an infected mother HIV can be passed from mother to.
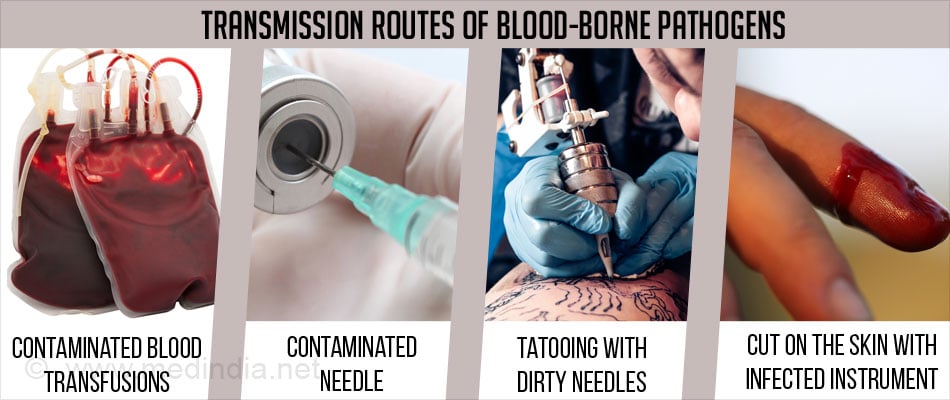
Blood Borne Diseases Transmission Types Diagnosis Prevention
If germs enter the body the bodys immune system begins to fight the disease.
. Any body fluid with blood is potentially infectious. OPIM includes the following. But HIV HBV and HCV are most common and they are the only ones that.
Within a healthcare environment needle pricks and accidental skin breaks from handling sharps instruments are common examples of bloodborne pathogen infections. Bloodborne Pathogens can be transmitted when blood or body fluid from an infected person enters another persons body via needle-sticks human bites cuts abrasions or through mucous membranes. Accidental puncture from contaminated needles broken glass or other sharps Contact between broken or damaged skin and infected body fluids.
Other transmission risks include. Contaminated instrument injuries A break in the skin cut lesion etc Mucus membranes eyes nose mouth Other modes. What Are Bloodborne Pathogens.
Part of an indirect transmission path bloodborne pathogens can be spread through the following paths. The most common and dangerous germs spread through blood in the hospital are. The most common ways bloodborne pathogens spread are through sexual transmission or IV drug use.
Transmission methods include. From mother to baby in breast milk. 1-5 BBPs of primary concern include HBV hepatitis C virus HCV and human immunodeficiency.
For a bloodborne pathogen to be spread the bodily fluids of an infected person must enter into the. The most common are bacteria and viruses. Bloodborne pathogens can enter your body through.
Common body fluids which can transmit pathogens include. In the health care setting bloodborne pathogens are often transmitted by percutaneous injury accidental puncture human bites cuts abrasions or through mucocutaneous exposure to infected patients fluids. - from mothers to their babies at or before birth.
The transmission of bloodborne pathogens from one person to another occurs through the transfer of infected body fluids. Semen Vaginal secretions Cerebrospinal fluid. Follow standard precautions to help prevent the spread of bloodborne pathogens and other diseases.
HIV human immunodeficiency virus. Bloodborne pathogens are bacteria and viruses present in blood. In the health care setting bloodborne pathogens are often transmitted by percutaneous injury accidental puncture human bites cuts abrasions or through mucocutaneous exposure to infected patients fluids.
Methods of Transmission cont. There are a variety of bloodborne pathogens such as syphilis malaria brucellosis. In the workplace the major source of bloodborne infections is percutaneous injuries from needles or other sharps.
A person inhales droplets from an infected person such as through a cough or sneeze. Also semen vaginal secretions and saliva in dental procedures are considered potentially infected body fluids. Working in a healthcare setting transfusion dialysis acupuncture tattooing and sharing razors or toothbrushes with an infected person.
These viruses cause infections and liver damage. Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens are microorganisms that are transmitted through the bloodstream. Most infectious diseases are caused by one of several types of pathogens.
Bloodborne pathogens are also transmitted in the following ways. With the correct information irrational fears about workplace exposure to HIV and HBV can be prevented. - through mucous membranes of the eyes nose or mouth such as by a splatter of contaminated blood.
Signs or symptoms of these diseases you should consult your physician or doctor as soon as possible. A vaccine is currently available for HBV. Health care workers emergency response and public safety personnel and other workers can be exposed to blood through needlestick and other sharps injuries mucous membrane and skin exposures.
Sharing a drinking glass with an infected person. Semen and vaginal secretions can transmit bloodborne pathogens but only during sexual contact. Modes of Transmission Bloodborne pathogens such as HBV and HIV can be transmitted through contact with infected human blood and other potentially infectious body fluids such as.
- sharing of hypodermic needles. Help keep pathogens from entering the body. Workers and employers should take.
Germs that can have a long-lasting presence in human blood and disease in humans are called bloodborne pathogens. Photo by Jason Rogers in Creative Commons Photo by Sharonoa Gott in Creative Commons. However any contact with infected blood or body fluids carries the risk of potential infection.
The pathogens of primary concern are the human immunodeficiency virus HIV hepatitis B virus HBV and hepatitis C virus HCV. Bloodborne pathogens are most commonly transmitted through. Transmissions of blood-borne pathogens BBPs in a dental health care setting have rarely been reported particularly since routine hepatitis B virus HBV vaccination of dental health care personnel DHCP and universal precautions were recommended 1982 and 1987 respectively.
Hepatitis B virus HBV and hepatitis C virus HCV. BBPs also known as bloodborne pathogens are microorganisms such as bacteria or viruses that are transmitted via human blood and other fluids that can cause disease. The viruses that cause Hepatitis B Virus HBV and Human Immuno-deficiency Virus HIV are two examples of bloodborne pathogens.
Direct blood contact with infected blood or blood products. HBV is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids such as semen and vaginal fluids.
0 Response to "Bloodborne Pathogens Are Transmitted by Which of the Following Methods"
Post a Comment